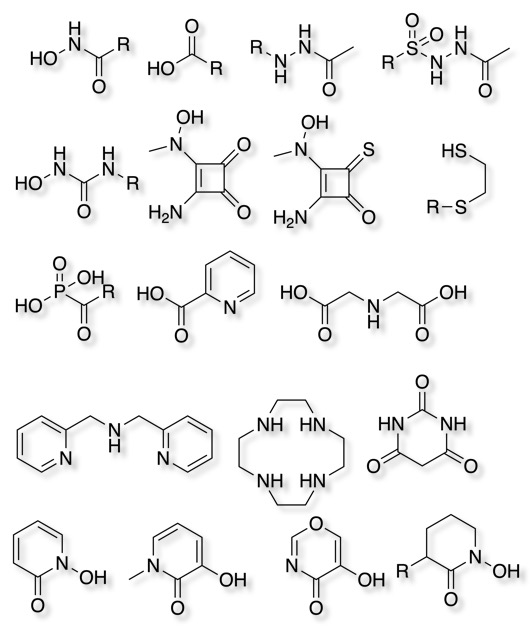
Metalloenzyme inhibitors
Most metalloproteases require zinc, but some use cobalt. The metal ion is usually coordinated to the protein via three ligands. The ligands coordinating the metal ion can vary with histidine, glutamate, aspartate, lysine, and arginine. The first generation of mall-molecule inhibitors was mimics of the natural peptide substrates of MMPs that were combined with a hydroxamic acid zinc-binding group to chelate the catalytic Zn2+ ion and inactivate the protein.
Interestingly, of the 137 NMEs approved by the FDA between 2013 and 2017 , 13 target metalloenzymes, representing 7% of the drugs DOI. Some examples that bind to the metal in the active site are shown below.
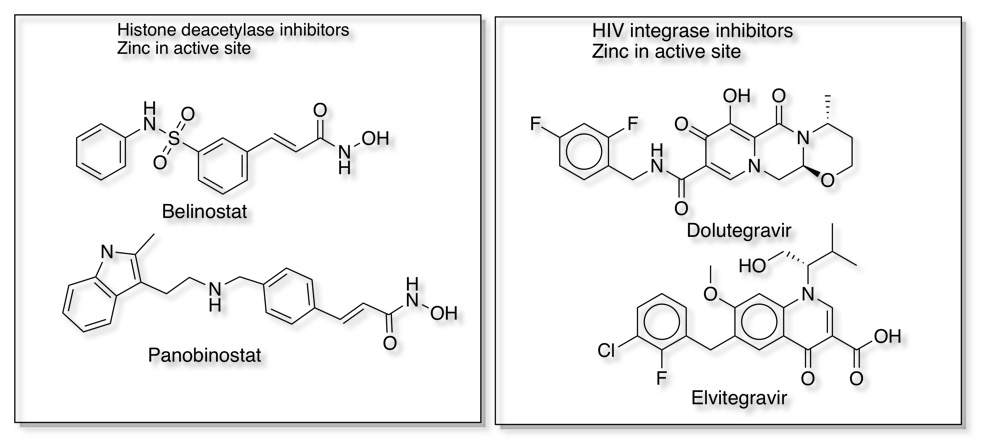
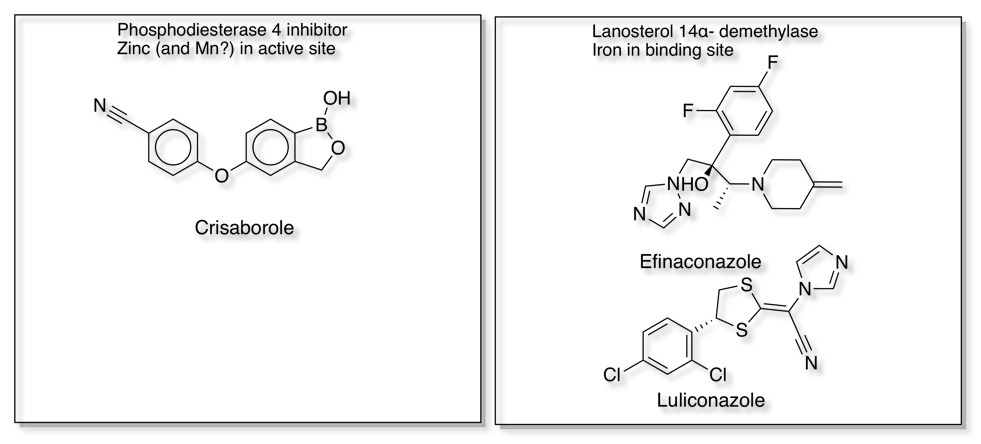
Metalloproteases
Metalloproteases are a class of enzymes that hydrolyse peptides, they all have a critical metal (usually Zinc but sometimes Cobalt) in the active site that is involved in the enzyme mechanism, The ligands coordinating the metal ion can vary with histidine, glutamate, aspartate, lysine, and arginine.
The catalytic mechanism is shown below. A water molecule activated by an active site histidine attacks the carbonyl of the scissile amide bond. The carbonyl of the amide coordinates to the Zinc to stabilise the oxyanion. The tetrahedral oxyanion then initiates elimination of the amine of the amide which then is protonated by the histidine. The protonation and deprotonation of the histidine is aided by a neighbouring acid.
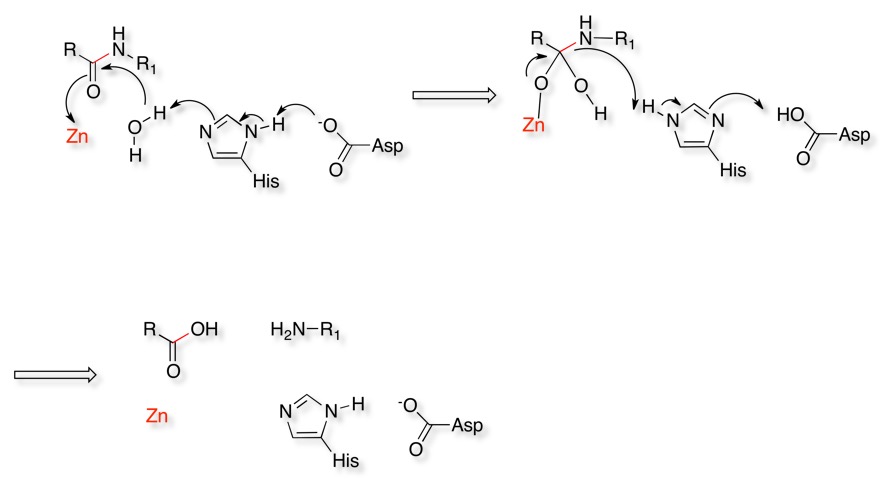
For more information on the mechanism have a look at the MACiE database (Mechanism, Annotation and Classification in Enzymes), Thermolysin, PDB entry 4TLN is an example of an Metalloprotease.
Inhibitors
Since metalloproteases contain a metal in the active site they can be inhibited by metal chelators or by compounds that can coordinate to the Zinc. The first generation of mall-molecule inhibitors was mimics of the natural peptide substrates of MMPs that were combined with a hydroxamic acid zinc-binding group to chelate the catalytic Zn2+ ion and inactivate the protein. Several hydroxamic acid derivatives have been reported to be potent inhibitors and shown to act as 1,4-bidentate ligands for the zinc. A number of matrix metalloprotease inhibitors have entered clinical trials for an oncologic indication including Batimastat and Marimastat however selectivity over the different matrix metalloproteinases can be problematic. Batimastat IC50 MMP-1 = 3 nM, MMP-2 = 4 nM, MMP-3 = 20 nM, MMP-8 = 10 nM, MMP-9 = 10 nM
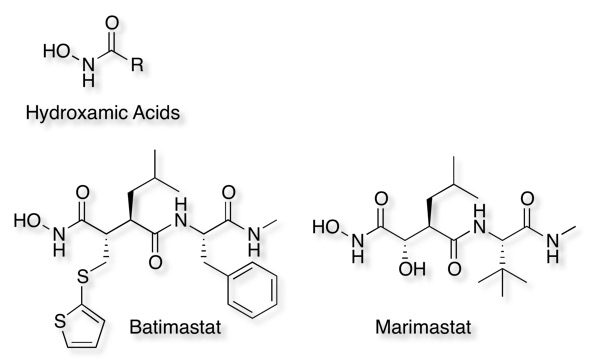
A range of other Zinc binding groups have been identified.
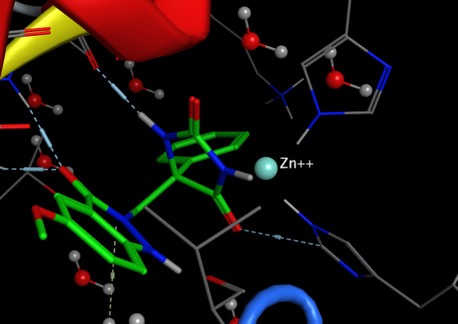
Another metalloprotease is Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE), ACE is a Zinc-dependent dipeptidyl carboxyl metallopeptidase that converts the decapeptide Angiotensin I to the octapeptide Angiotensin II. The structure of the enzyme is shown below (pdb:1O8A) with the Zinc atom coloured red, His387 and His383 shown in blue and Glu411 red. An acetate shown in green completes the coordination to the Zinc. (This is displayed using 3Dmol.js http://3dmol.csb.pitt.edu ).
Mouse Controls
| Movement | Mouse Input | Touch Input | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rotation | Primary Mouse Button | Single touch | ||
| Translation | Middle Mouse Button or Ctrl+Primary | Triple touch | ||
| Zoom | Scroll Wheel or Second Mouse Button or Shift+Primary | Pinch (double touch) | ||
| Slab | Ctrl+Second | Not Available |
There are three main classes of ACE inhibitors based on the functional group that binds to the metal, sulfhydryl-, carboxyl-, and phosphoryl-based inhibitors.
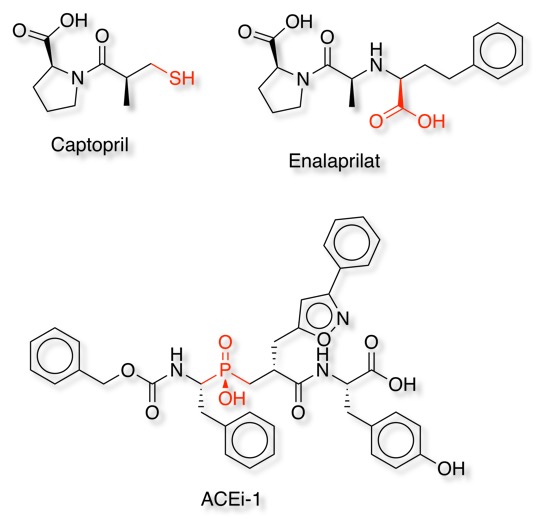
The structure of the enzyme bound to Enalaprilate is shown below (pdb:1UZE) with the Zinc atom coloured red, His387 and His383 shown in blue and Glu411 red. Enalaprilate is shown in green replacing the acetate in the structure above and coordinating to the Zinc.
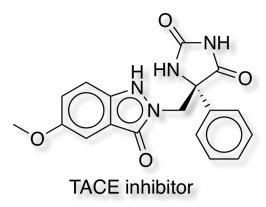
A series of by aryl hydantoins have been reported as TNF-α convertase enzyme (TACE) inhibitors DOI sub-nanomolar Ki, good rat P. In these compounds the hydantoin binds to the zinc.
See also metal chelation
Useful resource MetLigDB is a publicly accessible web-based database on which the interactions between a variety of chelating groups and various central metal ions in the active site of metalloproteins can be explored in detail. Additional information can also be retrieved including protein and inhibitor names, the amino acid residues coordinated to the central metal ion, and the binding affinity of the inhibitor for the target metalloprotein.
Worth Reading
Targeting Metalloenzymes for Therapeutic Intervention DOI
To bind zinc or not to bind zinc: An examination of innovative approaches to improved metalloproteinase inhibition DOI.
Updated 9 Fen 2023